
India’s growing cities are struggling with large, old dumpsites that have been collecting waste for decades. These sites, known as legacy waste, pose serious risks to the environment and public health. They occupy vast land areas, release harmful gases, and pollute soil and groundwater.
To tackle this issue, biomining of legacy waste in India has emerged as a sustainable and practical solution. It not only helps clean up existing waste but also allows for land recovery and pollution control.
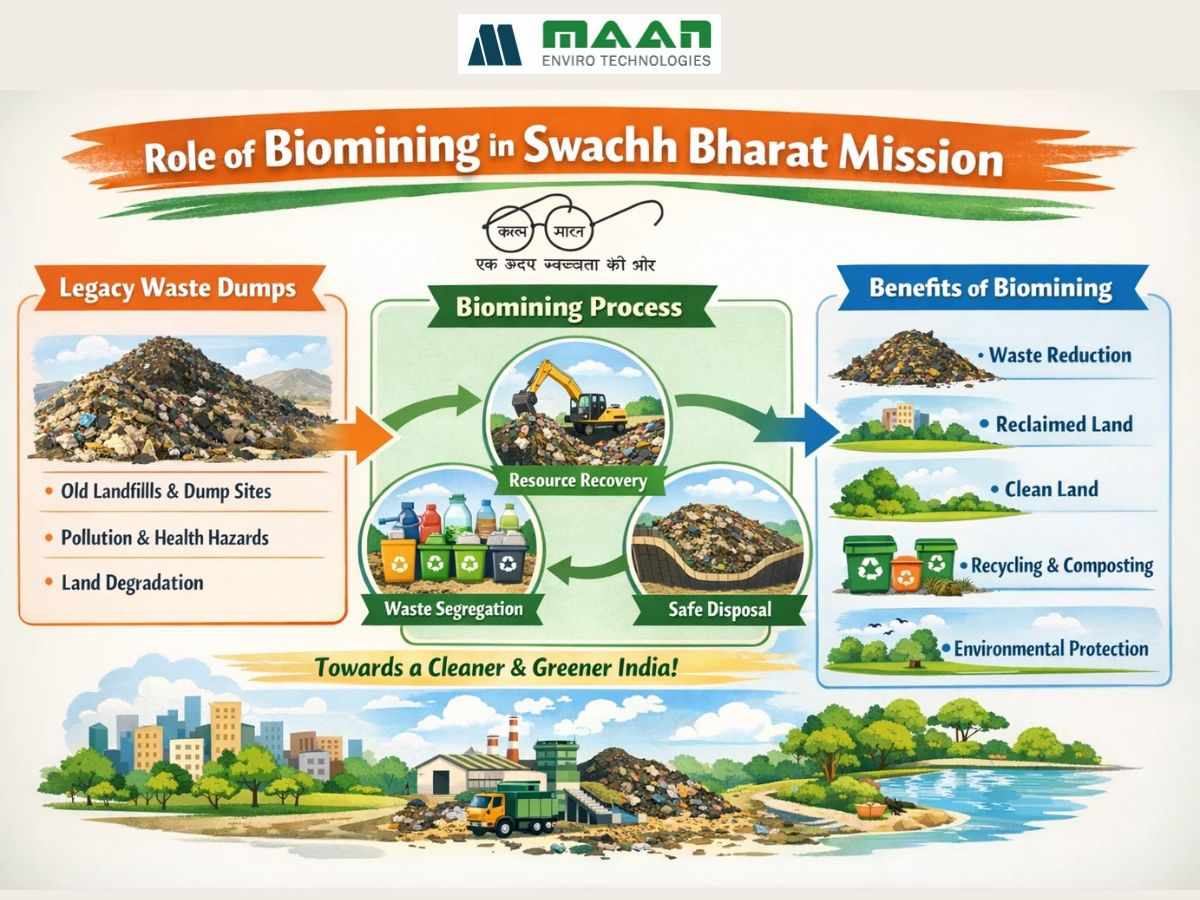
What Is Legacy Waste?
Legacy waste is old, untreated solid waste found in open dumpsites or landfills. It includes household garbage, industrial waste, plastics, soil, and other mixed materials that were never processed. Many of these dumps have been in use for over 10 to 30 years, especially near growing cities.
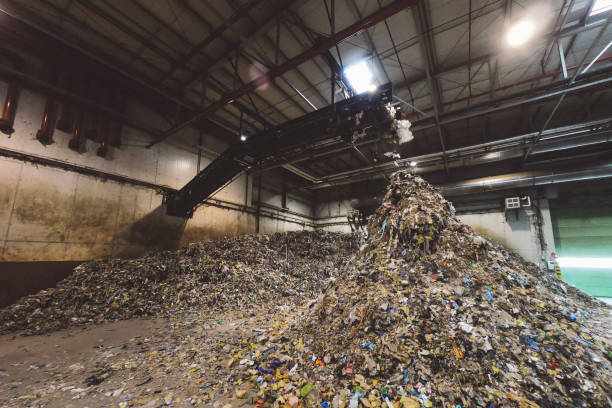

This waste slowly releases methane and toxic liquids that pollute the air, water, and land, making nearby areas unsafe.
What Is Biomining and How Does It Work?
Biomining is a method used to scientifically sort and treat legacy waste. Instead of burning or burying it, biomining separates compostable, recyclable, and non-usable materials using machines and simple biological treatment.
Common steps in biomining:
Excavation of waste using loaders and excavators
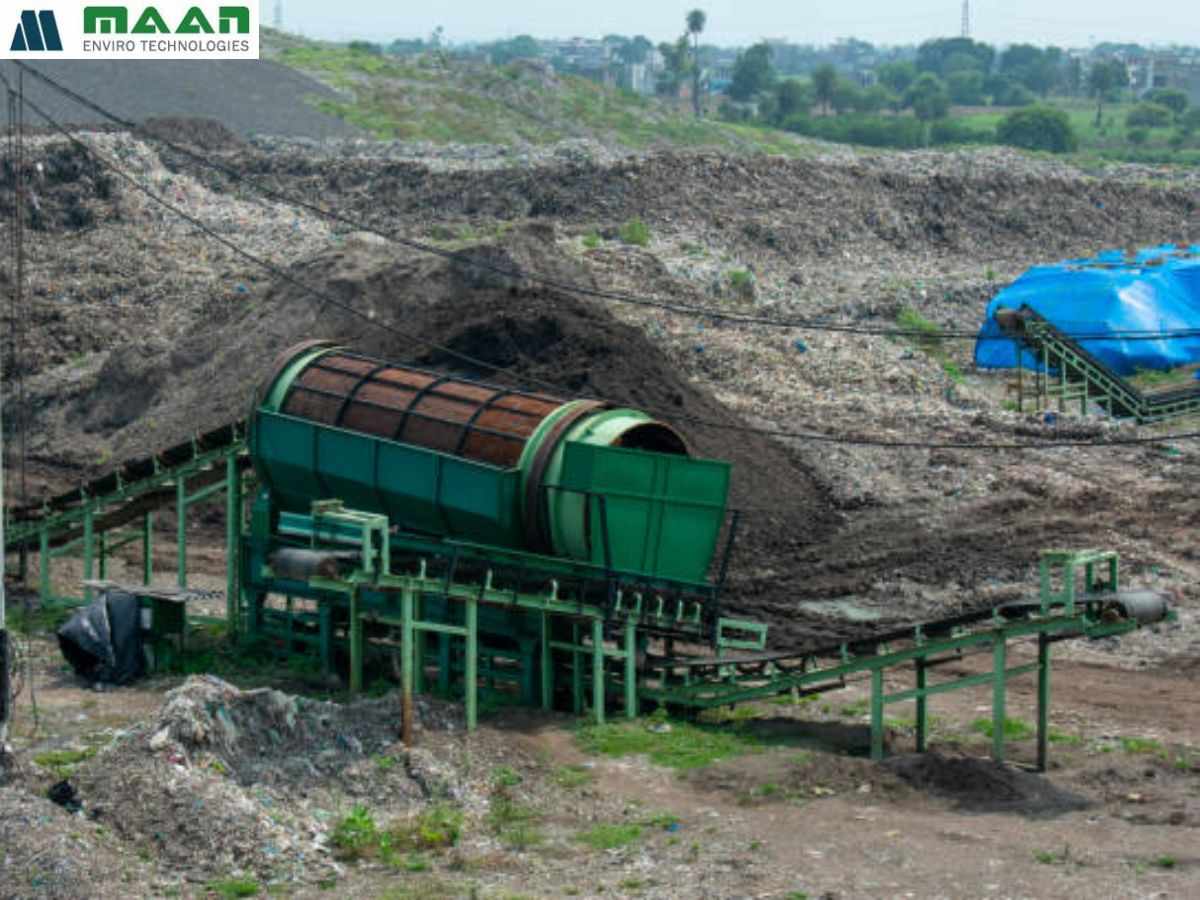
Screening with trommel machines to separate plastics, compost, soil, and debris
Recovery of compost-like material for use in parks or landfills
Recycling of metal, glass, and plastic
Safe disposal of non-recoverable waste
This method avoids creating more pollution and helps convert dumpsites into usable land.
Why Is Biomining Important for India?
1. Land Reclamation
Old dumps occupy valuable space in cities. Biomining clears these areas so the land can be reused for development, green zones, or public projects.
2. Pollution Reduction
Legacy dumps release toxic gases and liquids into the environment. Biomining helps cut down this pollution and improves air and water quality in nearby areas.
3. Material Recovery
Recyclable items like plastics and metals are recovered during the process. This supports recycling and reduces the need for raw materials.
4. Legal Compliance
Biomining supports the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016. Municipalities using biomining meet national waste clearance goals and avoid penalties.
Progress of Biomining of Legacy Waste in India
Several cities have started using biomining to treat old waste.
Examples:
Indore cleared over 13 lakh metric tonnes of waste and restored large areas of land
Gurugram and Faridabad are working on biomining at Bandhwari landfill
Chandigarh, Bhopal, and Nagpur have active biomining sites with ongoing progress
These projects show that biomining is a practical way to deal with legacy waste across different city sizes.
Common Challenges in Biomining
While biomining is effective, it does come with some challenges:
Mixed waste makes sorting difficult
Rainwater and leachate increase processing time
Many sites lack trained workers or the right machines
Government approvals and planning can delay progress
With better planning and proper support, these issues can be managed.
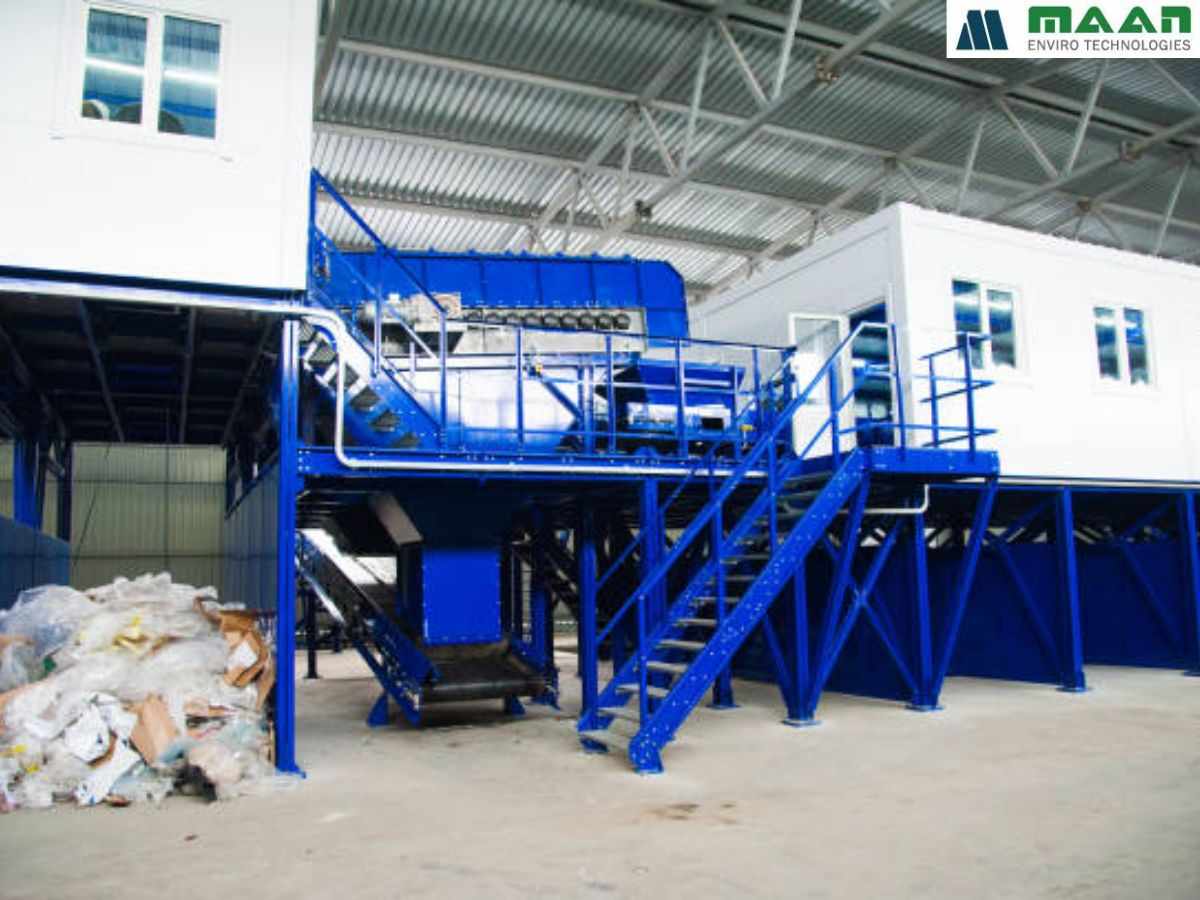
Equipment Used in Biomining Projects
A range of equipment is needed to manage legacy waste properly.
Trommel Screens to separate different waste types
Excavators and Loaders to dig and move waste
Shredders to break down bulky materials
Conveyor Belts for handling screened waste
Baling Machines to compact recyclable materials
At Maan Enviro Technologies, we supply durable machines designed for Indian waste conditions. Our equipment supports clean and safe operations across various biomining sites.
How Can Biomining Restore Old Dumps?
Biomining not only clears waste but also restores the area for future use. The land can be used for parks, gardens, storage, or even buildings, depending on the local plan.
To learn more, visit our guide on
👉 How Can Biomining Effectively Restore India’s Legacy Waste Sites?
FAQs on Biomining of Legacy Waste
1. What types of waste are found in legacy dumpsites?
These sites often include plastics, metals, glass, soil, organic waste, cloth, and other materials.
2. How long does a biomining project take?
The timeline depends on the size of the site. Small sites can take a few months, while large city dumps may take over a year.
3. What happens to recovered materials?
Soil-like material is reused for land cover. Plastics and metals go for recycling. Inerts are sent for safe disposal.
4. Is biomining a permanent solution?
It removes old waste, but new waste must be handled properly every day. Cities must follow good waste segregation and collection practices.
5. Can small towns also adopt biomining?
Yes. Small towns can run smaller biomining projects with the help of local machinery and government support.
Final Thoughts
Biomining is a smart and sustainable way to deal with India’s legacy waste. It helps free up land, reduce pollution, and recover useful materials. With proper support, more cities and towns can adopt this method and move towards cleaner surroundings.










Write a comment ...